How to Get Rid of Double Vision? Causes,Treatments, and FAQs
AUTHOR
Ophthalmologist/ Eye Surgeon 13+ Years Exp
MBBS, MS – Ophthalmology
TSMC- TSMC/FMR/05251 (2018)
TREATMENT
CALL US 24/7 FOR ANY HELP
GET IN TOUCH ON
Double vision, also known as diplopia, can be distressing and disruptive to everyday life. Whether you’ve noticed it gradually or been taken by surprise,
you may feel concerned about its implications and desperate for relief.
Fortunately, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help you take informed steps toward resolving this issue safely and effectively.
This guide provides an in-depth look at how to get rid of double vision, with professional insights and practical advice.
What Is Double Vision?
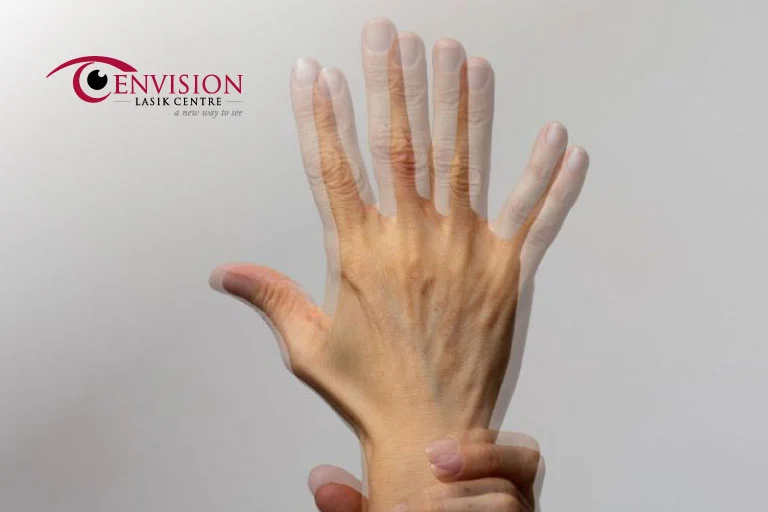
Double vision occurs when you see two images of a single object. The images may appear side by side, on top of each other, or at a diagonal.
It can impact one eye (monocular diplopia) or both eyes (binocular diplopia) and significantly affect your ability to drive, read, and perform other daily tasks.
While double vision can sometimes resolve on its own, it’s often a symptom of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. Recognising its type and root causes can help guide effective treatment.
Fast Fact: Over 800,000 individuals in the US seek professional care for double vision annually, making it a common ophthalmologic concern.
Causes of Double Vision
Different mechanisms underlie monocular and binocular double vision, necessitating tailored approaches for each.
1.Monocular Causes
Monocular diplopia persists even when one eye is closed. It is usually linked to structural abnormalities or issues in the affected eye, such as:
- Astigmatism: An irregularly curved cornea leading to distorted light projection.
- Cataracts: Cloudy lenses that scatter light, causing overlapping images.
- Keratoconus: A cone-shaped cornea can distort vision in one eye.
- Dry Eyes: Insufficient tear production can create uneven refractions of light.
2.Binocular Causes
Binocular diplopia, which disappears when covering one eye, arises from misalignment between the eyes. Common causes include:
- Strabismus: Misaligned eye muscles make both eyes point in different directions.
- Stroke or Brain Injury: Damage to the cranial nerves controlling eye movement can result in double vision.
- Thyroid Disease (e.g., Graves’): Swelling or inflammation in the eye muscles.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis can weaken eye control.
⇔Key Insight: Binocular causes are generally more serious than monocular ones and may indicate systemic health problems.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
⇒Symptoms of Double Vision
Symptoms vary depending on the underlying cause of diplopia. Common complaints include:
- Overlapping or side-by-side images.
- Dizziness and headaches.
- Reduced depth perception, making movement or driving difficult.
- Eye fatigue, particularly when focusing for extended periods.
⇒Child-Specific Symptoms
Children may not articulate their symptoms. Watch for signs like squinting, tilting the head, or closing one eye.
⇒Diagnosis
Medical evaluation starts with distinguishing between monocular and binocular double vision. Your provider may use the following tests and tools for diagnosis:
- Visual Acuity Tests: Determines how sharp your vision is.
- Eye Alignment Assessment: Identifies whether eye muscles are coordinated.
- Neurological Exams: Screens for possible brain or nerve-related causes.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans can identify structural issues, such as tumors or brain injuries.
Pro Tip: Always inform your eye specialist about accompanying symptoms like weakness, nausea, or slurred speech, as these could point to serious medical emergencies.
Treatment Options
Effectively treating double vision involves both addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms to improve quality of life.
⇒Non-Surgical Treatments
- Glasses with Prisms:
- A prism bends light, aligning images and reducing the visual burden.
- Temporary Fresnel prisms can easily be adjusted during the diagnostic phase.
- Occlusion Therapy (Eye Patch):
- Patching or covering one eye may block the extra image for temporary relief.
- Used in conditions like severe strabismus.
- Medications:
- Corticosteroids manage inflammation in thyroid-related double vision.
- Myasthenia gravis and similar disorders may benefit from immune-modulating drugs.
- Vision Therapy:
- Exercises can strengthen eye muscles, helping address convergence insufficiency.
- Exercises can strengthen eye muscles, helping address convergence insufficiency.
- Botox Injections:
- Temporarily relaxes overactive eye muscles in cases of severe misalignments.
⇒Surgical Treatments
For conditions unresponsive to nonsurgical management, ophthalmologists may recommend surgery, such as:
- Strabismus Surgery: Adjusts eye muscles to improve alignment.
- Cataract Removal Surgery: Improves clarity by replacing cloudy lenses.
- Neurological Surgery: Addresses issues like aneurysms or growing tumors affecting eye control.
Note: Each treatment plan is customised based on the severity and underlying cause of double vision.
Living with Double Vision
Managing life with diplopia requires practical adjustments to minimise risks and maintain independence. Tips include:
- Avoid driving until your doctor clears you for safe vision.
- Use extra lighting for tasks like walking or reading.
- Take regular breaks from screens to prevent eye strain.
FAQs About Double Vision
1.Why has my double vision started suddenly?
Sudden onset of diplopia can signify neurological emergencies, such as strokes, so immediate medical attention is essential.
2.Can stress or fatigue cause double vision?
Yes, extreme physical exhaustion or stress can temporarily trigger eye misalignment due to weakened control. Rest often helps.
3.How long does double vision last?
Duration depends entirely on the cause. While minor issues resolve in a few days, others may require prolonged interventions.
4.What if I have double vision after a head injury?
Seek emergency care immediately, as it could indicate severe trauma requiring prompt treatment.
When to See a Specialist
Call your doctor if your double vision persists beyond a day or is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Severe headache or nausea.
- Muscle weakness or paralysis.
- Impaired balance or coordination.
For emergencies like double vision combined with slurred speech or confusion, head straight to the ER.
Summary and Next Steps
Double vision can range from being a minor inconvenience to a sign of a serious medical condition. While temporary episodes may not require treatment, persistent cases deserve a thorough evaluation to uncover underlying causes.
With advancements in medical technology, effective treatments, including glasses, therapy, and surgery, offer hope for most individuals.
Take Action: If you experience double vision, schedule an appointment with an eye care professional today. Don’t delay diagnosing and addressing this treatable condition.
Your vision matters. Book your consultation now.
AUTHOR
Ophthalmologist/ Eye Surgeon 13+ Years Exp
MBBS, MS – Ophthalmology
TSMC- TSMC/FMR/05251 (2018)
TREATMENT
CALL US 24/7 FOR ANY HELP
GET IN TOUCH ON